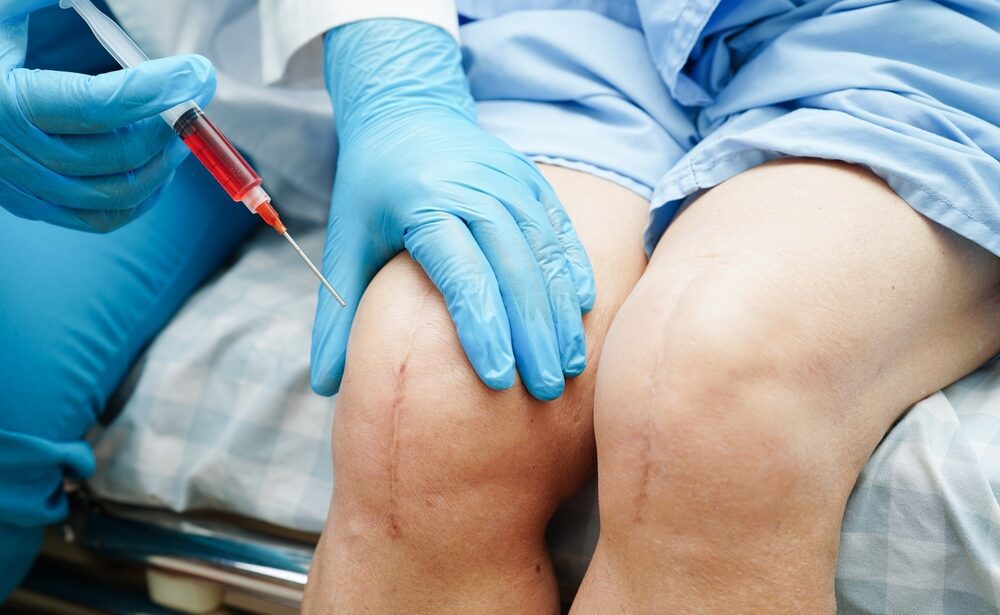
Overview
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is an innovative treatment that utilizes the patient’s own blood components to promote healing, reduce inflammation, and enhance tissue regeneration. By concentrating the platelets and growth factors in the blood, PRP therapy aims to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes and improve recovery from various musculoskeletal injuries and conditions.
Indications for Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy may be indicated for a variety of conditions, including:
- Tendon Injuries: Treatment of tendonitis or tears in areas such as the Achilles tendon, elbow (tennis elbow), or shoulder (rotator cuff).
- Joint Conditions: Management of osteoarthritis and other degenerative joint diseases, particularly in the knee, hip, and shoulder.
- Soft Tissue Injuries: Healing of muscle strains, ligament sprains, and other soft tissue injuries.
- Chronic Pain: Relief for patients with chronic pain conditions related to musculoskeletal disorders.
- Aesthetic Applications: Enhancing skin rejuvenation and hair restoration in cosmetic procedures.
Components of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- Blood Collection:
- A small volume of the patient’s blood is drawn, typically from the arm, using standard blood collection techniques.
- This process is quick and minimally invasive.
- PRP Preparation:
- The collected blood is processed using a centrifuge to separate the platelets and plasma from other blood components (red blood cells and white blood cells).
- The result is a concentrated solution rich in platelets and growth factors, ready for injection.
- Injection Procedure:
- The prepared PRP is injected directly into the target area, such as the injured tendon, joint, or soft tissue.
- The procedure may be guided by ultrasound imaging to ensure accurate placement and maximize treatment effectiveness.
- Post-Procedure Care:
- Patients are typically advised to rest the treated area and avoid strenuous activities for a short period following the injection.
- Pain or swelling at the injection site may occur but usually resolves within a few days.
- Follow-Up Assessments:
- Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the patient’s response to therapy and assess improvements in pain and function.
- Additional PRP injections may be considered based on the patient’s progress and specific condition.
Benefits of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- Natural Healing: As the treatment uses the patient’s own biological material, there is a lower risk of allergic reactions or complications associated with foreign substances.
- Reduced Inflammation: PRP contains anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate pain and inflammation in injured tissues.
- Enhanced Recovery: PRP therapy may accelerate the healing process for musculoskeletal injuries and conditions, leading to improved recovery times.
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure is relatively quick and involves minimal downtime compared to traditional surgical options.
Possible Risks and Limitations
- Variable Results: The effectiveness of PRP therapy can vary among individuals and may depend on factors such as the type of injury, severity, and overall health.
- Mild Discomfort: Some patients may experience discomfort, swelling, or bruising at the injection site, although these effects are usually temporary.
- Not Suitable for Everyone: Certain conditions or medical histories may limit a patient’s eligibility for PRP therapy.
Final Results
Through PRP therapy, patients can expect:
- Pain Relief: Reduction in pain levels and improvement in overall function of the affected area.
- Enhanced Healing: Stimulation of the body’s natural healing processes, potentially leading to faster recovery from injuries.
- Improved Quality of Life: Increased mobility and ability to perform daily activities without discomfort.